London underwent massive suburban expansion in the interwar period. The interwar period saw a combination of an increase of Londoners who were looking for suitable living space; an increase in disposable income and a reduction of housing costs; and a greater availability of accessible building plots around the outskirts of the city. These factors led to a veritable suburban ‘boom’ during the 1920s and 1930s, at the end of which London’s size had increased threefold and the population of its suburbs had grown by 2.5 million compared to the start of the century.[1]
The first London suburbs were built by private investors during the nineteenth century, when the introduction of tramcars and other modes of public transport opened up areas further away from the city centre, for residential development. By the end of the nineteenth century the London County Council also ordered the development of suburban estates, to provide healthier living quarters to poorer Londoners.[2] These two types of suburbs – private developments and council estates – continued to co-exist in the Edwardian and interwar periods. Private developments were mostly aimed at the aspirational middle-classes, who would look to mortgage a semi-detached or detached house.
Elsewhere in this blog I have considered how the suburbs were represented on film; how tennis was a key social activity for suburbanites; how an expansion of car ownership changed the entertainment opportunities open to suburban Londoners and how the experience of suburban women was captured in interwar novels. The suburbs, in short, were on the forefront of social changes and the experiences of their inhabitants provided inspiration for artists.
Yet suburbs were also synonymous with boredom and small-mindedness, particularly to the urban intelligentsia.[3] Privately developed suburbs were built by builders and speculators, who bought up cheap land, built houses on them, and then sought to sell these brand new dwellings as quickly as possible. One of the key ways they used to entice Londoners to buy a suburban house was to present suburbia as a rural environment.
‘Most advertisements and brochures were accordingly illustrated with idealised sketches or heavily retouched photographs which skilfully suggested that the house stood quite along in matured surroundings of judiciously placed trees and shrubs, against a background of windblown clouds and gently rolling hills.’[4]
In London’s north-western corner, new estates serviced by the Metropolitan Railway were quickly badged up as part or ‘Metro-land’. Transport posters presented this new land as a rural idyll with ‘Gorgeous Autumnal Scenery’ and ‘Charming Country Walks’; as well as an excellent place to go fishing. At Radlett, near Watford, a developer promised such aristocratic pursuits as ‘Hunting, Shooting, Beagling and the like….every phase of rural life at Radlett provides the perfect antidote to business worries.’[5] At the same time, it was crucial that suburban estates had quick and easy transport lines into the centre of London. Here, misleading advertisements could be the developer’s friend: brochures and advertisements frequently cited the fastest possible travel time as standard, even if most of the daily trains would take much longer to get to the city.[6]
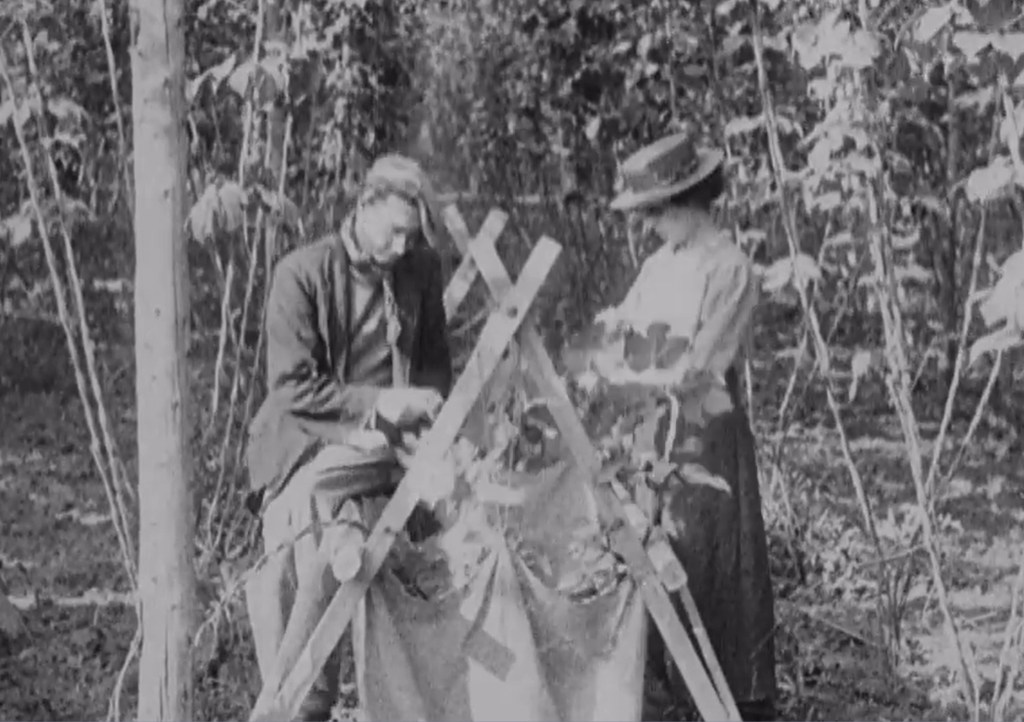
Because suburbs kept expanding incessantly, any estate that started out as a semi-rural enclave would quickly find itself engulfed by other estates, the ‘rolling hills’ and ‘mature trees’ covered by more semi-detached housing. Most suburban dwellers were exposed to nature primarily through their garden. Because suburban houses were often built in styles to remind people of cottages and other old-fashioned houses, historian Matthew Hollow has argued that ‘the move out to the cottage estate was accompanied by a desire to indulge in new, more family-centred, pastimes. Gardening became a popular family pastime for many.’[7] Gardening also allowed suburban houseowners to express their creativity and compete with their neighbours in popular and wide-spread estate garden shows.[8] Perhaps surprisingly, in the popular imagination the garden became the domain of the male head of the household, retreating to the garden after dinner to tend to his plants. As ever, London Underground’s poster designers had their finger on the pulse with this 1933 poster, showing a city man seamlessly transforming into a suburban gardener mowing his lawn.
One final way in which suburban inhabitants themselves sought to underline the rural character of their neighbourhoods was through their house names. As completely new developments, many privately-built suburban estates did not yet have properly assigned addresses when their first inhabitants moved in – another sign of the speed of suburban development, which outpaced the local authority administration. To ensure their homes could be identified, many suburbanites named their own houses, and names such as ‘Meadowside’, ‘Woodsview’ and ‘Fieldsend’ both highlight the semi-rural nature of the suburban environment, and indicate that for the people living in these houses, the natural surroundings were significant.
Despite its sometimes negative reputation, suburban living was a dream for many working- and middle-class Londoners during the interwar period; a dream encouraged by the sometimes fanciful advertising techniques used by speculative developers. For many, suburban living offered a first chance of home ownership, and access to private green space. The vast suburban developments of the 1920s and 1930s continue to shape London to this day.
[1] Mark Clapson, Suburban Century: Social change and urban growth in England and the United States (Oxford: Berg, 2003), p. 2; Stephen Halliday, Underground to Everywhere (Sutton: Stroud, 2001), p. 113
[2] Peter Hall, Cities of Tomorrow (Oxford: Blackwell, 2002) pp. 21 and 50-52
[3] Alan A. Jackson, Semi-Detached London (London: George Allen & Unwin, 1973), p. 162
[4] Ibid., p. 204
[5] Ibid., p. 205
[6] Ibid., p. 206
[7] Matthew Hollow, ‘Suburban ideals on England’s interwar council estates’, Garden History, vol. 39, no. 2 (2011), 203-217 (213)
[8] Ibid., p. 209